| Issue |
EPJ Web Conf.
Volume 168, 2018
Joint International Conference of ICGAC-XIII and IK-15 on Gravitation, Astrophysics and Cosmology
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | 08005 | |
| Number of page(s) | 8 | |
| Section | Cosmology | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/201816808005 | |
| Published online | 09 January 2018 | |
https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/201816808005
Accelerated cosmological expansion without tension in the Hubble parameter*
Fast evolution of the Hubble parameter H(z)
614 Yeongsil-Gwan, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Sejong University, 143-747 Seoul, South Korea
** e-mail: mvp@sejong.ac.kr
Published online: 9 January 2018
The H0-tension problem poses a confrontation of dark energy driving latetime cosmological expansion measured by the Hubble parameter H(z) over an extended range of redshifts z. Distinct values H0 ≃ 73 km s–1 Mpcs–1 and H0 ≃ 68 km s–1 Mpcs–1 obtain from surveys of the Local Universe and, respectively, ΛCBM analysis of the CMB. These are representative of accelerated expansion with H′(0) ≃ 0 by 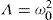 and, respectively, H′(0) > 0 in ΛCDM, where
and, respectively, H′(0) > 0 in ΛCDM, where 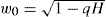 is a fundamental frequency of the cosmological horizon in a Friedmann-Robertson-Walker
universe with deceleration parameter q(z) = -1 + (1+z)H–1 H′(z). Explicit solution H(z) = H0
is a fundamental frequency of the cosmological horizon in a Friedmann-Robertson-Walker
universe with deceleration parameter q(z) = -1 + (1+z)H–1 H′(z). Explicit solution H(z) = H0 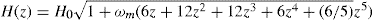 and, respectively, H(z) = H0
and, respectively, H(z) = H0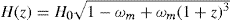 are here compared with recent data on H(z) over 0 ≲ z ≲ 2.The first is found to be free of tension with H0 from local surveys, while the latter is disfavored at 2:7σ A further confrontation obtains in galaxy dynamics by a finite sensitivity of inertia to background cosmology in weak gravity, putting an upper bound of m ≲ 10–30 eV on the mass of dark matter. A C0 onset to weak gravity at the de Sitter scale of acceleration adS = cH(z), where c denotes the velocity of light, can be seen in galaxy
rotation curves covering 0 ≲ z ≲ 2 Weak gravity in galaxy dynamics hereby provides a proxy for cosmological evolution.
are here compared with recent data on H(z) over 0 ≲ z ≲ 2.The first is found to be free of tension with H0 from local surveys, while the latter is disfavored at 2:7σ A further confrontation obtains in galaxy dynamics by a finite sensitivity of inertia to background cosmology in weak gravity, putting an upper bound of m ≲ 10–30 eV on the mass of dark matter. A C0 onset to weak gravity at the de Sitter scale of acceleration adS = cH(z), where c denotes the velocity of light, can be seen in galaxy
rotation curves covering 0 ≲ z ≲ 2 Weak gravity in galaxy dynamics hereby provides a proxy for cosmological evolution.
© The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2018
 This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.



