| Issue |
EPJ Web of Conferences
Volume 66, 2014
INPC 2013 – International Nuclear Physics Conference
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | 07010 | |
| Number of page(s) | 4 | |
| Section | Nuclear Astrophysics | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/20146607010 | |
| Published online | 20 March 2014 | |
https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/20146607010
Measurement of the 13C(α, n)16O reaction at astrophysical energies using the Trojan Horse Method. Focus on the -3 keV sub-threshold resonance
1 Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare, Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, Catania, Italy
2 Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia, Università di Catania, Catania, Italy
3 Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare, Sezione di Perugia, & Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Perugia, Perugia, Italy
4 Institute of Nuclear Research (ATOMKI), Debrecen, Hungary
5 Department of Physics, Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida, USA
6 Cyclotron Institute, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, USA
a e-mail: lacognata@lns.infn.it
Published online: 20 March 2014
Most of the nuclei in the mass range 90 ≲ A ≲ 208 are produced through the so-called s-process, namely through a series of neutron capture reactions on seed nuclei followed by β-decays. The 13C(α, n)16O reaction is the neutron source for the main component of the s-process. It is active inside the helium-burning shell of asymptotic giant branch stars, at temperatures ≲ 108 K, corresponding to an energy interval of 140 − 230 keV. In this region, the astrophysical S(E)-factor is dominated by the −3 keV sub-threshold resonance due to the 6.356 MeV level in 17O. Direct measurements could not soundly establish its contribution owing to the cross section suppression at astrophysical energies determined by the Coulomb barrier between interacting nuclei. Indirect measurements and extrapolations yielded inconsistent results, calling for further investigations. The Trojan Horse Method turns out to be very suited for the study of the 13C(α, n)16O reaction as it allows us to access the low as well as the negative energy re- gion, in particular in the case of resonance reactions. We have applied the Trojan HorseMethod to the 13C(6Li, n16O)d quasi-free reaction. By using the modified R-matrix approach, the asymptotic normalization coefficient 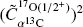 of the 6.356 MeV level has been deduced as well as the n-partial width, allowing to attain an unprecedented accuracy for the 13C(α, n)16O astrophysical factor. A preliminary analysis of a partial data set has lead to
of the 6.356 MeV level has been deduced as well as the n-partial width, allowing to attain an unprecedented accuracy for the 13C(α, n)16O astrophysical factor. A preliminary analysis of a partial data set has lead to 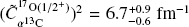 slightly larger than the values in the literature, determining a 13C(α, n)16O reaction rate in agreement with the most results in the literature at ∼ 108 K, with enhanced accuracy thanks to this innovative approach.
slightly larger than the values in the literature, determining a 13C(α, n)16O reaction rate in agreement with the most results in the literature at ∼ 108 K, with enhanced accuracy thanks to this innovative approach.
© Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2014
 This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.



