| Issue |
EPJ Web Conf.
Volume 234, 2020
International Workshop on “Flavour Changing and Conserving Processes” (FCCP2019)
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | 01013 | |
| Number of page(s) | 6 | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/202023401013 | |
| Published online | 27 April 2020 | |
https://doi.org/10.1051/epjconf/202023401013
Dispersion relations for hadronic light-by-light and the muon g − 2
1
Fakultät für Physik, Universität Wien, Boltzmanngasse 5, 1090 Wien, Austria
2
University of Bern, Sidlerstrasse 5, 3012 Bern, Switzerland
3
Institute for Nuclear Theory, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195-1550, USA
4
Department of Physics,University of California at San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093, USA
a e-mail: mprocura@univie.ac.at
b e-mail: gilberto@itp.unibe.ch
c e-mail: mhofer@uw.edu
d e-mail: pstoffer@ucsd.edu
Published online: 27 April 2020
The largest uncertainties in the Standard Model calculation of the anomalous magnetic moment of the muon (g−2)µ come from hadronic effects, namely hadronic vacuum polarization (HVP) and hadronic lightby-light (HLbL) contributions. Especially the latter is emerging as a potential roadblock for a more accurate determination of (g−2)µ. The main focus here is on a novel dispersive description of the HLbL tensor, which is based on unitarity, analyticity, crossing symmetry, and gauge invariance. This opens up the possibility of a data-driven determination of the HLbL contribution to (g−2)µ with the aim of reducing model dependence and achieving a reliable error estimate.
Our dispersive approach defines unambiguously the pion-pole and the pion-box contribution to the HLbL tensor. Using Mandelstam double-spectral representation, we have proven that the pion-box contribution coincides exactly with the one-loop scalar-QED amplitude, multiplied by the appropriate pion vector form factors. Using dispersive fits to high-statistics data for the pion vector form factor, we obtain 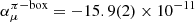 . A first model-independent calculation of effects of ππ intermediate states that go beyond the scalar-QED pion loop is also presented. We combine our dispersive description of the HLbL tensor with a partial-wave expansion and demonstrate that the known scalar-QED result is recovered after partial-wave resummation. After constructing suitable input for the γ*γ* → ππ helicity partial waves based on a pion-pole left-hand cut (LHC), we find that for the dominant charged-pion contribution this representation is consistent with the two-loop chiral prediction and the COMPASS measurement for the pion polarizability. This allows us to reliably estimate S-wave rescattering effects to the full pion box and leads to
. A first model-independent calculation of effects of ππ intermediate states that go beyond the scalar-QED pion loop is also presented. We combine our dispersive description of the HLbL tensor with a partial-wave expansion and demonstrate that the known scalar-QED result is recovered after partial-wave resummation. After constructing suitable input for the γ*γ* → ππ helicity partial waves based on a pion-pole left-hand cut (LHC), we find that for the dominant charged-pion contribution this representation is consistent with the two-loop chiral prediction and the COMPASS measurement for the pion polarizability. This allows us to reliably estimate S-wave rescattering effects to the full pion box and leads to 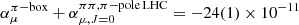 .
.
© The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2020
 This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.



